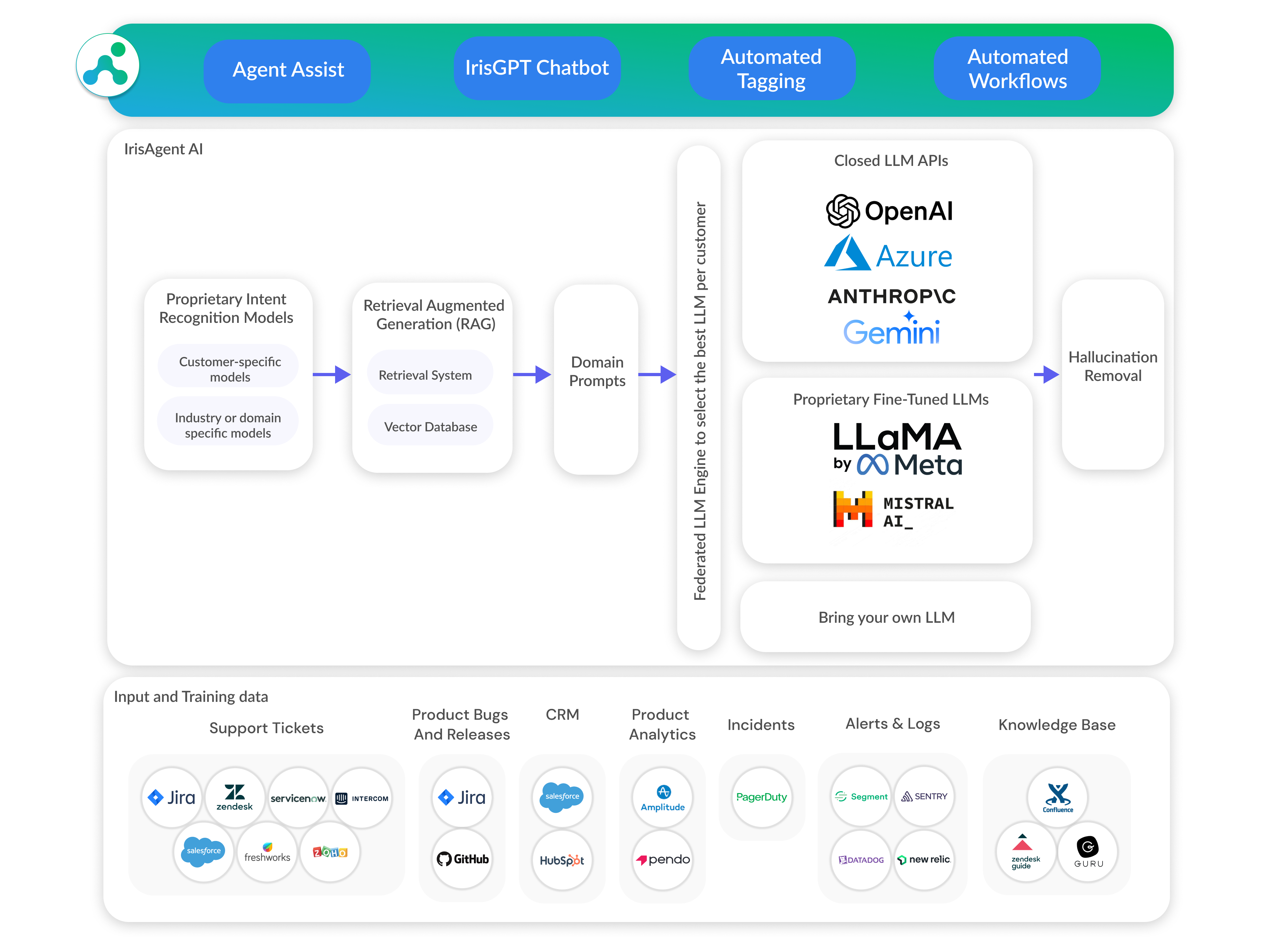
What is NLU: Explore the Core of Natural Language Understanding
What is NLU? At its most basic, Natural Language Understanding (NLU) is a critical AI technology that enables computers to interpret human language. The core components of NLU include natural language input and output, which are essential elements that allow machines to analyze, interpret, and generate human language across various devices and platforms. Throughout this article, we’ll explore how NLU works, why it’s fundamental to AI advancement and its real-world applications.
Key Takeaways
Natural Language Understanding (NLU) is an AI subfield focusing on enabling machines to understand human language in its natural form, aiming to achieve human-like interaction with computers across various contexts and large datasets.
NLU involves sophisticated tasks such as parsing, sentiment analysis, entity recognition, and semantic role labeling, and makes use of processes like tokenization, lexical, syntactic, and semantic analysis for a comprehensive understanding of language.
Despite NLU’s wide-ranging applications in industries like customer service, healthcare, and social media monitoring, it faces challenges such as interpreting ambiguous phrases, detecting sarcasm, and accommodating diverse languages and dialects.
Defining Natural Language Understanding (NLU)
So, what exactly is Natural Language Understanding (NLU)? At its core, NLU is a subfield of artificial intelligence and computer science that focuses on teaching software to understand sentences, be it in text or speech form. The grand objective of NLU? To enable human-like communication with computers, making it easier for machines to comprehend our natural language and respond accordingly. However how natural language understanding is achieved remains a complex challenge in the field of computer science and artificial intelligence, which brings us to the language understanding NLU definition.
After analyzing natural language input, NLU systems create an internal representation of meaning, allowing machines to interpret and generate appropriate responses.
NLU is more than just processing natural language input. It is about producing intelligent and actionable output, such as answering a query, by understanding human language in its natural form. NLU maps various linguistic elements, such as syntax and parts of speech, to enable computers to understand and process language. Moreover, NLU is not just about individual records; it also involves understanding context across larger datasets at scale. NLU uses machine learning algorithms to transform unstructured speech or written language into a structured data model. NLU also faces challenges in processing different languages due to unique grammatical structures and cultural nuances.
The Importance of NLU
Given what NLU can do, it’s easy to see why it has become critical in the business environment. Utilizing NLU can provide businesses with a competitive edge by offering new insights that guide better decision-making. It’s not just about automating processes; it’s about enhancing the interactions between businesses and consumers.
NLU is used in various industries, prominently in customer service applications. For example, through sentiment analysis, NLU can help companies understand customer attitudes and net promoter scores by:
Providing a deeper understanding of customer sentiments
Guiding businesses in improving their services
Enhancing customer satisfaction.
NLU vs. NLP vs. NLG
While the terms Natural Language Understanding (NLU), Natural Language Processing (NLP), and Natural Language Generation (NLG) are often used interchangeably, they each have distinct roles in the realm of language technology. NLP is the broader field encompassing systems designed to understand human language in general, and it includes a wide range of nlp tasks such as syntax analysis, sentiment analysis, and language translation. NLP also covers foundational tasks like part of speech tagging, which involves identifying the grammatical components of sentences. NLU is a specialized component that specifically focuses on comprehending the meaning and intent behind human language input, making natural language understanding important.
On the other hand, NLG is another specialized component of NLP, but its focus is on generating natural language output that can replicate human-like text. Natural Language Generation (NLG) crafts a human-sounding response based on the understanding derived from NLU. This technology is used in various applications, like composing news articles or creating personalized content based on data and user interactions.
The Mechanics of Natural Language Understanding
Understanding how NLU works is like peeling back the layers of an onion. It involves several tasks, including:
Parsing
Sentiment analysis
Named entity recognition
Entity recognition
Semantic role labeling
NLU relies on various machine learning approaches, such as statistical models and deep learning, to analyze text data from sources like social media and customer feedback.
All of these tasks work together to process and understand human language. Let’s delve into these mechanics to get a clearer picture of how NLU makes sense of our words and sentences.
Parsing is the process of breaking down sentences into smaller parts to understand their structure and meaning. After parsing and tokenization, embedding algorithms convert each token into a numerical representation that is plotted onto a vector space to map relationships between tokens. Word embeddings like Word2Vec and GloVe map words into dense vector spaces where similar meanings lie closer together.
Sentiment analysis involves determining the attitude, emotions, and opinions within the text. Sentiment analysis is the application of machine learning models to identify mood and emotion in a piece of content.
Named entity recognition identifies and classifies key information such as names, locations, dates, and brands within the text, serving as a crucial step in extracting structured data for further semantic analysis and intent recognition.
Entity recognition identifies and categorizes specific entities within the text, such as names, locations, dates, and brands.Semantic role labeling involves identifying the semantic relationships among the words in a sentence, which helps the system understand the roles that different words play in the sentence.
Intent recognition identifies the user's goals or purposes within a conversation or query, helping categorize user input to facilitate appropriate responses or actions in dialogue systems or search applications.
Tokenization and Lexical Analysis
Tokenization is a foundational process in NLU. It’s like breaking a sentence into individual pieces - words, characters, or subwords, ready for further analysis. There are three broad categories of tokenization: word tokenization, character tokenization, and subword tokenization.
After tokenization, lexical analysis comes into play. This process involves determining the parts of speech of individual tokens and understanding their grammatical structure, intention, and entities mentioned. For example, a special type of tokenization, known as subword tokenization, is used to handle Out Of Vocabulary (OOV) words using known subwords, contributing to the effectiveness of intent and entity recognition within NLU.
Syntactic and Semantic Analysis
After tokenization and lexical analysis, syntactic and semantic analysis come into play. In syntactic analysis, NLU examines the structure of a sentence to understand the grammatical relationships between words and ensures that the word arrangement follows proper computer language syntax rules. Syntax level ambiguity occurs when the meaning of a sentence depends on the arrangement of words.
Semantic analysis, on the other hand, digs deeper. It delves into the meaning behind words and sentences, exploring how the meanings of individual words combine to convey the overall sentence meaning. NLU must resolve multiple meanings of words—also known as lexical ambiguity—such as the word 'bank' referring to a financial institution or the side of a river, depending on context. Understanding linguistic nuances, such as homonyms and context, is essential for accurate semantic analysis. This part of NLU is vital for understanding the intent behind a sentence and providing an accurate response. Human language is fluid, complex, and full of subtleties, making it challenging for machines to grasp.
Intent and Entity Recognition

Once tokens are analyzed syntactically and semantically, the system then moves to intent recognition. This step involves identifying user sentiment and pinpointing the objective behind textual input by analyzing the language used. NLU models are trained for accurate intent recognition and emotional effort intent understanding by using training data consisting of example user utterances categorized by intent.
Simultaneously, entity recognition categorizes specific named entities like names and locations and identifies numeric entities such as dates and percentages. Methods such as regular expressions, lookup tables, and the BILOU tagging schema are leveraged in NLU for precise identification and extraction of entities.
Machine Learning and Deep Learning in NLU
Machine learning and deep learning are at the heart of modern Natural Language Understanding (NLU) systems, empowering computers to accurately interpret human language. Machine learning algorithms use statistical methods to process data, recognize linguistic patterns, and assign meaning to words and phrases within context. This allows NLU systems to move beyond simple keyword matching and truly understand the intent behind natural language input.
Deep learning, a specialized branch of machine learning, leverages artificial neural networks to capture complex relationships and dependencies in language. These deep learning models excel at tasks like sentiment analysis, where they can detect subtle emotional tones in text, and are instrumental in powering advanced applications such as speech recognition, machine translation, and virtual assistants. By continuously learning from vast datasets, NLU systems become more adept at language understanding, enabling machines to respond appropriately to user requests and perform tasks with greater accuracy.
As NLU technology evolves, the integration of machine learning and deep learning continues to enhance the capabilities of chatbots, virtual assistants, and other AI-driven solutions, making them more effective at interpreting and processing natural language in real-world scenarios.
NLU and Human Language
Natural Language Understanding (NLU) is fundamentally about bridging the gap between human language and machine comprehension. Human language—whether spoken, written, or shared through social media posts—is rich with nuance, ambiguity, and context. NLU systems use advanced computational linguistics and sophisticated algorithms to break down this complexity, enabling machines to interpret human language with remarkable accuracy.
Through intent recognition, NLU systems can determine what a user wants, while entity recognition identifies key information such as names, dates, or locations within a conversation. Sentiment analysis further allows NLU to gauge the emotional tone behind user requests. By analyzing both spoken language and written language, NLU algorithms can process unstructured data from a variety of sources, including customer emails, chat logs, and social media posts.
The ultimate goal of NLU is to enable machines to respond appropriately to user intent, making them capable of performing tasks like language translation, speech recognition, and text classification. This makes NLU a critical component of artificial intelligence, powering applications that require a deep understanding of human communication and context.
Real-World Applications of NLU
From data capturing to voice-controlled home appliances, NLU is revolutionizing various aspects of our lives and industries. It’s improving healthcare by speeding up and enhancing the accuracy of analyzing electronic health records. In the mobility sector, NLU contributes to a more interactive driving experience through voice commands.
Search engines use NLU to analyze user queries and intent, delivering more relevant search results that improve user experience and engagement. Voice assistants like Google Assistant leverage NLU to recognize spoken commands and perform tasks such as scheduling and emailing, making daily routines more efficient. NLU enables chatbots to interpret and respond to human language, which improves customer support and experience management. In fact, customer support bots are expected to handle up to 80% of inquiries by 2025 using NLU. Smart home automation systems now allow users to search security footage using natural language, making it easier to find specific events. Banks utilize NLU to scan communications for unusual language patterns, helping to detect potential fraud.
NLU’s applications aren’t limited to these. It’s used in pilot simulation training to enable voice interaction, thereby enhancing the effectiveness of the training programs. In the era of Industry 4.0, NLU is empowering workers to use natural language for interacting with inventory management systems and enhancing collaboration with robots through voice commands.
Chatbots and Virtual Assistants
One of the most noticeable applications of NLU is in chatbots and virtual assistants. By utilizing NLU, chatbots can interact with humans in unsupervised settings, improving the functionality and accessibility of customer support. Systems like Alexa and interactive voice response (IVR) can process human language, direct customer calls, and minimize the time users spend seeking support.
The integration of NLU in conversational interfaces allows for a more natural interaction where the virtual assistants understand the context and intent behind users’ spoken language. The incorporation of NLU in chatbots and virtual assistants leads to a more streamlined customer experience, enabling businesses to focus on growth and customers to maximize product use.
Sentiment Analysis and Social Media Monitoring
In the realm of social media, NLU plays a crucial role in sentiment analysis and monitoring. By categorizing comments and monitoring social media feedback, NLU technology aids brands in assessing their perception in the market. With NLU, analysts can distill large volumes of unstructured text into coherent groups, bypassing the need to read through each entry individually.
Advanced NLU tools, such as Watson Natural Language Understanding, provide deep insights into language data through analysis of:
categories
concepts
entities
keywords
relationships
sentiment
syntax
This in-depth customer experience analysis allows brands to better understand their customers and tailor their marketing strategies accordingly.
Machine Translation and Multilingual Support
Breaking language barriers is another incredible application of NLU. It leverages machine learning algorithms to provide more accurate language translation across various languages, enhancing communication globally. Machine translation enables the automatic conversion of text from one language to another, making it easier for people and businesses to communicate across borders. For global businesses, it’s crucial to select NLU solutions that are scalable and offer support for multiple languages and dialects to ensure inclusive user interactions.
Customer Experience and NLU
Natural Language Understanding (NLU) is transforming the way businesses interact with their customers, delivering more personalized and efficient experiences. By leveraging NLU-powered chatbots and virtual assistants, companies can analyze customer feedback, perform sentiment analysis, and recognize user intent in real time. This allows businesses to respond appropriately to customer requests, resolve issues faster, and provide tailored recommendations that boost customer satisfaction.
NLU systems excel at processing unstructured data, such as social media posts and open-ended survey responses, extracting actionable insights that help organizations understand customer preferences and pain points. With advanced intent recognition and entity recognition, NLU algorithms enable machines to handle a wide range of customer inquiries, from simple tasks to complex problem-solving, all while maintaining a natural and conversational tone.
As more businesses adopt NLU technology, the ability to deliver 24/7 support, reduce operational costs, and enhance the overall customer experience becomes a key differentiator in competitive markets. By enabling machines to understand and process natural language, NLU is setting a new standard for customer engagement and satisfaction.
NLU and Healthcare
Natural Language Understanding (NLU) is making significant strides in the healthcare industry, offering powerful tools for analyzing and interpreting vast amounts of clinical data. NLU algorithms can process unstructured information from doctor-patient conversations, medical notes, and lab reports, uncovering patterns and insights that support clinical decision-making and medical diagnosis.
In addition to data analysis, NLU-powered chatbots are being used to engage patients, provide personalized health advice, and facilitate communication between patients and healthcare providers. These virtual assistants can interpret patient queries, deliver relevant information, and help manage appointments or medication reminders, improving patient engagement and satisfaction.
NLU also plays a crucial role in medical research by analyzing medical literature, summarizing clinical trials, and identifying relevant findings for healthcare professionals. By enabling machines to understand and process natural language, NLU helps healthcare providers stay informed, make better decisions, and deliver more personalized care. The integration of NLU in healthcare not only enhances the quality of care but also streamlines operations and reduces costs, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes.
Challenges and Limitations of NLU
Despite its immense potential, NLU is not without its challenges. NLU systems face significant challenges such as lexical ambiguity, syntax ambiguity, referential ambiguity, and linguistic diversity, which make accurately interpreting natural language difficult. One of the significant hurdles in NLU is interpreting ambiguous phrases that have multiple potential meanings. This can lead to misunderstanding the user’s intent. Semantic analysis in NLU is also challenged by the need to appreciate context beyond literal word meanings. Capturing dependencies between words, especially long-range relationships, is crucial for maintaining contextual accuracy in NLU. Transformer based models like BERT and GPT excel at capturing long-range dependencies in text, enabling better contextual understanding. Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) analyze text sequentially and maintain context, with variants like LSTM and GRU handling long-term dependencies. Additionally, unsupervised learning techniques show algorithms massive unlabeled datasets to discover underlying relationships and patterns.
Homonyms and synonyms are significant sources of confusion for NLU, as they require the system to discern meaning from words that sound the same or have similar meanings but are used in different contexts. Moreover, detecting irony and sarcasm in language is particularly challenging for NLU, as the intended meaning is often the opposite of the literal words used.
NLU systems also encounter difficulties with human language text, especially in text-to-speech and speech-to-text conversions due to human speech pronunciation variations, accents, slang, and idioms that diverge from standard language rules. These challenges can be addressed by implementing advanced speech recognition technology.
Future Trends and Developments in NLU

Looking ahead, NLU promises exciting advancements. Transformer models like BERT and GPT-3 are increasing the scope of context interpretation in text, paving the way for more complex multimodal AI systems. Developments in zero-shot and few-shot learning demonstrate a movement towards systems that can understand new tasks with minimal training data.
Simultaneously, there’s a growing concentration on ethical AI with ongoing efforts to reduce biases within language models to make NLU technologies fairer and more accurate. Advancements in multilingual NLU capabilities are paving the way for high-accuracy language analysis across a broader spectrum of languages. However, NLU technologies face challenges in supporting low-resource languages spoken by fewer people and in less technologically developed regions.
Selecting the Right NLU Solution for Your Business
Selecting the right NLU solution involves considering several factors. Sophisticated NLU solutions are capable of recognizing entities and relationships, understanding complex sentiment, making inferences, suggesting results, and having training and continuous learning capabilities. But, it’s not just about the capabilities; it’s also about the fit with your business’s industry, goals, and audience.
Custom NLU systems, developed specifically for a business’s needs, can significantly enhance performance and relevance. Ease of use and integration options are also critical for the easy adoption of NLU solutions within companies. Technical support and training availability are essential for an NLU solution provider to ensure effective utilization of the system.
Summary
In essence, NLU is revolutionizing how humans and machines interact. It’s transforming industries, enhancing customer experiences, and breaking language barriers. While it does face challenges, the future of NLU holds exciting possibilities. From advancements in transformer models to ethical AI, NLU is set to become even more integral in our lives and businesses. It’s not just about teaching machines to understand human language; it’s about building bridges, fostering understanding, and creating a future where communication with machines is as natural as talking to another human.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Natural Language Understanding (NLU)?
Natural Language Understanding (NLU) is a subfield of artificial intelligence that aims to teach software to comprehend and interpret human language, enabling more effective interaction between humans and computers.
How does NLU work?
NLU works by processing and understanding human language through tasks like parsing, sentiment analysis, and entity recognition. It also involves semantic role labeling to achieve its goal.
What are the real-world applications of NLU?
NLU has a wide range of real-world applications, such as data capturing, voice-controlled devices, healthcare, and pilot simulation training, among others. These applications demonstrate the versatility and practical relevance of NLU in various industries.
What are the challenges and limitations of NLU?
The challenges of NLU include interpreting ambiguous phrases, understanding context, handling homonyms and synonyms, detecting irony and sarcasm, and dealing with pronunciation variations. These limitations make natural language understanding a complex task that requires ongoing improvements and advancements.
What are the future trends in NLU?
In the future, NLU will see advancements in transformer models, zero-shot and few-shot learning, ethical AI, multilingual capabilities, and support for low-resource languages. These developments will significantly shape the field of natural language understanding.