How Customer Service Automation Works: Benefits and Best Practices
Large and small businesses have had to re-look at their support automation processes and technology investments, given the promise of Generative-AI for support automation. Organizations now have easy access to generative AI technology - via DIY open-source projects or secure Enterprise Support Automation platforms like IrisAgent. But how does an organization get its support automation strategy and implementation right to improve customer satisfaction?
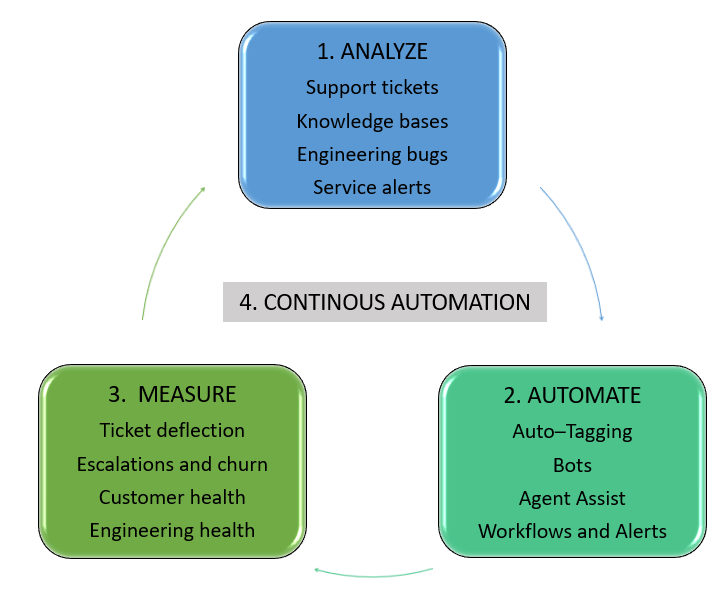
This comprehensive guide discusses the key steps to implement a successful customer service automation strategy. It outlines four key steps to using automated customer service software to use Generative-AI effectively.
Knowing how and where to start
Identifying what to automate
Key metrics to track progress
Establishing a continuous automation approach for long-term success
The process map below summarizes the steps above,
The following sections detail the steps above for customer service strategy, the best practices, and tips the IrisAgent team has learned to implement support automation for several clients.
Step 1: ANALYZE - Knowing how and where to start
Generative AI is powered by huge machine learning models pre-trained on vast amounts of data, referred to as foundation models (FMs). A subset of foundation models called large language models (LLMs) is trained on a large number of words across many natural-language tasks. In the case of support automation, LLMs are trained on historical customer support tickets and data as well as institutional knowledge. Thus, the first step in customer service automation is integrating key systems that hold this data. Following are the key systems to typically integrate with (Tip: take note of the uncommon, often missed out engineering systems),
CRM Systems: Starting with the obvious, most support organizations over the years have made significant investments in CRM systems, popular ones being Salesforce, Zendesk, Microsoft Dynamics, Intercom, ServiceNow, and Freshworks.
Best practice: Have at least one year of data made available to the LLM model in use.
Knowledge Bases/FAQs: These are either part of CRM systems, help documentation or articles available to support teams.
Best practice: Have at least one year of frequently accessed articles available to the LLM model in use
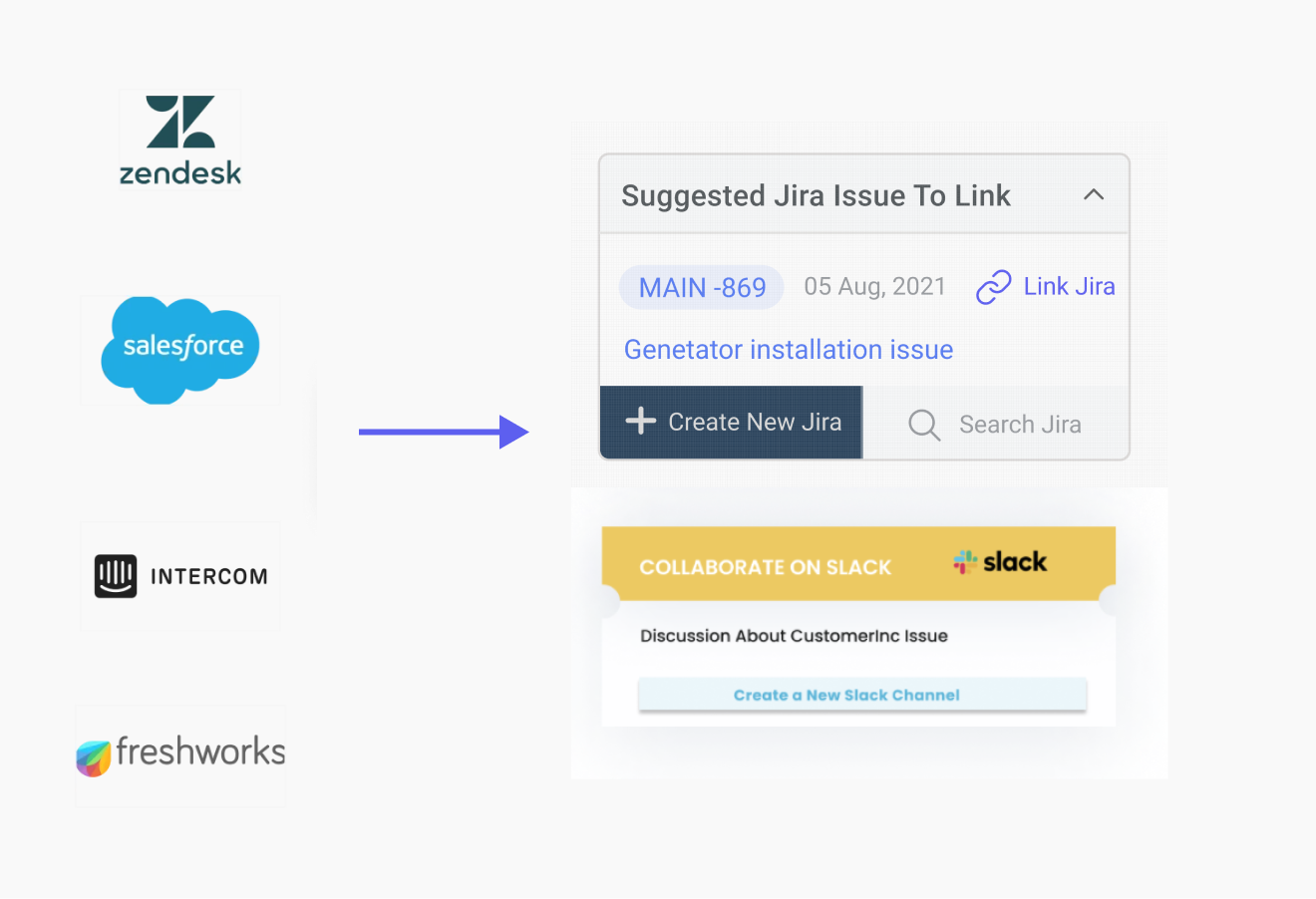
Engineering bugs: This area is often missed, but vast amounts of institutional knowledge are buried inside engineering bug-tracking software or project management software such as JIRA and Confluence by Atlassian.
Best practice: Have at least two years of product release-related information. We recommend more historical data access here as engineering systems often hold data that are precursors or predictors of issues that can be anticipated and potentially automated.
Service Alerts: In the case of enterprise SaaS, it is common to share service alerts internally and with customers via tools such as pagerDuty.
Best practice: Have at least three months of service alert information.
A key point to note: While integrating into CRM systems is obvious and low-hanging fruit, integrating Engineering bugs and Service Alerts should be an equal priority, as the most accurate institutional product knowledge base often lies with engineering and DevOps teams.
Step 2: AUTOMATE - Identifying what to automate
Once the first step of integrating the institutional knowledge is complete and your LLM model has access to rich historical data, the second step in customer service automation is to systematically analyze data, categorize it, and uncover what to automate vs. topics best left to human-assisted support. The following steps outline a reliable approach,
Auto-tagging - Helps classify content for keywords associated with root-cause analysis, correlations to existing issues, customer intent, and sentiment. Accuracy in tagging will form the foundation of the following three types of automation.
Full automation, i.e., no human intervention: Via bots, Intelligent Virtual Agents for Voice and digital support interactions. The frequency and recency of auto-tagging of content guide what should be fully automated. The IrisAgent platform specializes in auto-tagging, quickly highlights the top tags, and provides recommendations on what to automate to improve overall customer experience.
Best practice: Questions related to the top 5 tags in the last 6-12 months are great candidates to start full automation. In our experience, automating these delivers 40 to 50% ticket deflection. This is a good place to start. Anything beyond the top 5 does result in false positives and, unfortunately, the undesired consequence of a “bad bot experience” by customers. We do not recommend over-automating initially.
Agent Assist: This is where AI helps an agent address questions with potential answers in real time. Agent Assist is designed to aid the agent rather than take over fully automated customer service.
Best practice: Take the top 10 auto-tagged content from the past two years and deliver that as agent assist capability. IrisAgent provides this as a side-by-side widget inside CRM systems.
Workflows and alerts: This is the category where items not automated in the aforementioned steps are seamlessly handled via intelligent workflows that alert the right support representative of subject matter experts. IrisAgent platform allows for easy configuration of alerts and notifications to cross-functional teams.
Best practice: Implementing cross-functional workflows. Often, engineering teams are disconnected from the frontline. Alerting them promptly brings in SMEs sooner for a timely resolution. The IrisAgent platform was built with the premise that pulling in engineering knowledge early and often can result in effective support. IrisAgent platform provides robust OOB cross-functional workflows and alerts, ready to use up deployment.
Step 3: Key Metrics
Most traditional support operations measure ticket counts, response times, and SLA attainment and further drill down into product categories, severity, and regional performance in the case of distributed teams. With automated customer service, a new set of metrics has emerged. While we deal with information overload, we have identified the following key metrics for customer service automation,
Ticket Deflection Rate - i.e., how many customer interactions and questions got addressed without a human interaction Measures the effectiveness of automation via bots.
Mean Time to Resolution (MTTR) - The time it takes to solve an issue. This helps understand the efficacy of agent assistance and workflows implemented.
Escalations - Helps understand issues that remain unaddressed or indicate a broader CSAT problem.
Agent Performance - Helps understand if the customer service agents find the real-time assist technologies useful.
Engineering and Product Health - Ongoing incidents, Product status, and Historical incidents - Provides insights into overall product quality and effectiveness of engineering processes for development and quality assurance.
The above reports should be incorporated into weekly or monthly metrics tracking. The IrisAgent platform makes these available as part of out-of-the-box dashboards and reports.
Best Practice: Not too many companies track Engineering Health, which often is a leading indicator for issues that can be anticipated. We recommend adding this metric to your overall reporting. IrisAgent delivers this unique insight out of the box.
Step 4: Establishing continuous automation
Once an organization has implemented the above steps for customer service automation, monitoring metrics and changes to auto-tagging user data is important, and adapting the self-service automation mix accordingly.
Best practice: Establish a review every six months and make appropriate changes, i.e., automate new categories and simple tasks and move older categories to agent assist or to process workflows.
Here’s why you need customer service automation and AI in today’s economic climate
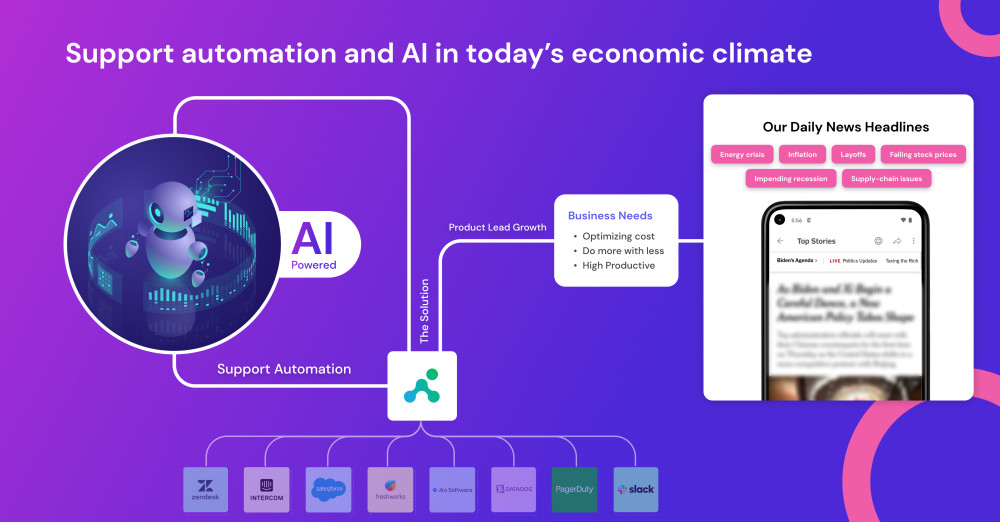
These days, headlines seem to be dominated by the geo-political crisis and unfavorable macroeconomic environment conditions - inflation, supply-chain issues, layoffs, impending recession, falling stock prices, energy crisis, and the list goes on and on. These tough conditions are forcing organizations to rethink their business plans. If there is a common theme today, it is about,
Optimizing for costs.
Doing more with less.
Ensuring employees are engaged and at their best productivity.
While the headlines may be negative, business leaders must remind themselves to “Never let a good crisis go to waste” - as Winston Churchill, the war-time prime minister of the United Kingdom, famously stated during World War II. In these situations, smart use of technology combined with optimized process engineering can help cut costs, keep employees engaged, drive productivity, keep customer service costs low, and ultimately help build a profitable business even in tough economic conditions.
At IrisAgent, AI-powered customer service automation software is built to deliver the outcomes above for the support channels, organizations, and services, especially with product-led growth companies. The IrisAgent platform helps organizations do more with less by
Applying AI to Support operations - automated tagging and correlation of issues in CRM systems with backend systems used by engineering and DevOps. IrisAgent supports all popular CRM systems, such as Salesforce, Zendesk, Freshworks, ServiceNow, and Intercom. Backend integrations with JIRA and PagerDuty.
Streamlined workflows between frontline customer service team and engineering team
Improve agent productivity and reduce resolution time by recommending related product bugs, answers, and articles.
Delivered product feedback as a closed-loop feedback mechanism to product managers and Customer Success Teams.
Examples of automated customer service in action
The significance of customer support cannot be overstated in the business landscape. As companies strive to enhance their service delivery and customer satisfaction, the adoption of automated customer service solutions plays a pivotal role. These innovative technologies streamline operations, reduce redundancy, and simplify complex processes. Below are prime examples of how automated customer service is revolutionizing the way businesses interact with their customers:
1. Chatbots on Websites: Many companies integrate AI-powered chatbots on their websites to provide instant responses to customer queries. These chatbots can be automated messages to handle a wide range of tasks from answering FAQs and guiding users through the website to initiating service requests, thereby improving efficiency and customer satisfaction.
2. Virtual Customer Assistants: Virtual assistants, powered by AI, can engage with customers through voice or text across various platforms and communication channels. They offer personalized support, suggest products based on customer preferences, and can even troubleshoot basic issues, enhancing the customer experience.
3. Automated Email Responses: Automated email systems can instantly acknowledge customer inquiries and complaints. They can provide estimated wait times for responses, direct customers to helpful resources, or escalate customer concerns and issues to human agents when necessary, ensuring customers feel heard and valued.
4. Self-Service Portals: Self-service portals empower customers to find solutions to their problems without directly interacting with customer service representatives. Customers can access FAQs, user manuals, forums, and instructional videos, fostering customer relationships and a sense of autonomy and satisfaction.
5. Social Media Monitoring Tools: These tools automatically scan social media platforms for mentions of the company, its products, or services. They can automatically respond to common questions, thank customers for positive feedback, or flag issues for human agents, maintaining a positive brand image.
6. Interactive Voice Response (IVR) Systems: IVR systems guide callers through a series of automated menus, allowing them to solve their issues, access information, or be directed to the appropriate contact center or department without human intervention. This technology streamlines call center operations and reduces wait times.
7. Ticketing Systems: Automated ticketing systems organize customer inquiries support requests and issues into tickets, which are then prioritized and assigned to the appropriate teams. This ensures that no customer query is overlooked and improves the efficiency of the response process.
8. Predictive Analytics for Customer Support: By analyzing customer data and past interactions, AI can predict potential customer issues, and offer proactive support solutions before the customer even reaches out, significantly enhancing the customer experience.
By incorporating these automated customer service solutions, businesses not only improve their operational efficiency but also significantly enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty. Automating routine tasks allows human customer service representatives to focus on more complex and high-value interactions, ensuring that every customer receives the attention and care they deserve.
Challenges and Considerations with Automated Customer Service
While the adoption of an example of automated services as customer service tools brings a plethora of benefits, it is not without its challenges and considerations. Understanding and addressing these aspects are crucial for a successful and sustainable implementation of automated services of customer service software.
A. Potential Pitfalls of Over-Reliance on Automation
Loss of Personalized Customer Service:
Automation may risk diluting the personal touch that human agents can provide. Customers often appreciate a personalized experience, and an overemphasis on automation might lead to a sense of detachment from customer requests.
Misinterpretation of Customer Intent:
While AI has made significant strides in natural language processing, there are instances where customer queries may be misinterpreted. This can result in inaccurate responses and, in some cases, frustration for the customer.
B. Ensuring Ethical and Responsible Use of AI in Customer Service
Transparency in Automation:
Customers may be uneasy if they are not aware they are interacting with a machine. Maintaining transparency about the use of automation and clearly communicating when a customer is engaging with AI is essential for building trust.
Data Privacy Concerns:
Automated systems often rely on large datasets to improve their performance. Ensuring the privacy and security of customer data is paramount to prevent potential breaches and unauthorized access.
C. Balancing Automation with Human Touch
Knowing When to Escalate to Human Agents:
There are situations where the complexity or sensitivity of an issue may require human intervention. Establishing a seamless transition between automated processes and human agents is crucial to prevent customer frustration.
Cultural Sensitivity:
Cultural nuances in language and communication can be challenging for automated systems to grasp accurately. This becomes particularly important in global customer service operations.
D. Adaptability to Changing Customer Expectations
Keeping Pace with Evolving Technology:
Customer expectations are dynamic, and technology evolves rapidly. Ensuring that automated systems can adapt to changing preferences and stay aligned with the latest advancements is a perpetual challenge.
Flexibility in System Configuration:
Rigidity in the automation system may hinder its ability to accommodate unique or evolving customer service requirements. A flexible and customizable approach is vital for long-term success.
E. Employee Engagement and Adaptation
Reskilling and Training:
Implementing automation may necessitate reskilling and training for human agents to collaborate effectively with automated systems. Resistance to change among employees can be a significant hurdle that requires careful management.
As businesses navigate the landscape of customer service automation, these challenges and considerations must be addressed thoughtfully. By doing so, organizations can harness the benefits of customer journey automation solutions while mitigating potential pitfalls, fostering a harmonious balance between technological efficiency and the human touch in customer service.
Ready to Automate Customer Service?
In conclusion, the aforementioned 4-step approach can enable the support team in your organization to implement a successful customer service strategy using Generative-AI technologies. The IrisAgent platform has been built around this 4-step approach and has successfully helped customer service teams implement Support Automation. We would love to help you get your own service experience and GenAI journey started!
Get started to automate, handle customer interactions and questions, and provide customer support and service the right way!
Automated Customer Service: Frequently Asked Questions
What is automated customer service, and how does it differ from traditional customer service?
Automated customer service refers to using technology, such as chatbots, virtual assistants, and automated phone systems, to assist customers in resolving their inquiries, issues, or requests without direct human intervention. Unlike traditional customer service, which relies heavily on human customer service agents for interactions, automated customer service operates 24/7, providing immediate responses, consistency in handling queries, and cost-efficiency. While traditional customer service offers a personal touch and nuanced problem-solving, we offer automated customer service systems that excel in handling routine, repetitive tasks, and customer service tasks, freeing up customer service teams to focus on more complex issues and value-added interactions.
What are the key advantages of implementing automated customer service systems?
Implementing automated customer service systems offers several key advantages for businesses. Firstly, it enables 24/7 availability, ensuring customers can get assistance anytime, enhancing customer satisfaction. Additionally, it reduces operational costs by automating routine tasks and queries, allowing companies to allocate resources more efficiently. Automation also ensures consistency in responses and excellent customer service quality. Moreover, it can simultaneously handle many service requests, reducing customer wait times. Automated customer service systems enhance efficiency, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness, making them valuable to modern customer service strategies.
What security measures should be in place to protect customer data when using automated systems?
Robust security measures in customer service automation should include data encryption in transit and at rest to safeguard it from unauthorized access. Access controls and authentication protocols should be in place to restrict system access to authorized personnel only. Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments can help identify and rectify potential weaknesses. Data anonymization techniques can also minimize the risk associated with storing sensitive information. Continuous monitoring of automated system and activity for any unusual patterns or breaches is essential, along with a well-defined incident response plan to address any security incidents promptly. Compliance with relevant data protection regulations, such as GDPR or HIPAA, is crucial to ensure the legal and ethical handling of customer data. A multi-layered security approach is vital to protect customer data in automated systems.
How can businesses measure the success and ROI of their customer service automation initiatives?
Metrics such as customer satisfaction scores (CSAT), Net Promoter Score (NPS), and customer effort score (CES) can gauge customer experience improvements. Tracking the reduction in customer service response times and call volume can indicate efficiency gains. Additionally, businesses should analyze cost savings from reduced labor and operational expenses. Evaluating the resolution rate of customer inquiries in a completely automated manner and comparing it with human-assisted customer service skills can reveal the effectiveness of various automation tools. Finally, monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) like conversion rates, upsell/cross-sell success, and customer retention can provide insights into the broader impact on revenue generation.
Can I speak to a live agent if needed?
Depending on the system, there may be an option to transfer to a live support agent if the automated service cannot resolve a particular issue. This ensures a seamless transition in customer interactions for users with more complex or personalized queries with support agents.
What is an example of automated customer service?
An example of automated customer service is a chatbot on a company's website. These chatbots use artificial intelligence to understand and respond to customer inquiries in real-time, providing information, answering common questions, and even handling certain tasks like booking appointments or processing returns without the need for a human customer service representative.
How can I provide feedback on Automated Customer Service interactions?
Feedback mechanisms are often integrated into Automated Customer Service platforms. For example, customers can typically provide feedback to live agents through surveys or rating systems, helping improve the system's performance over time. With IrisAgent's AI platform, customer service teams can provide customer feedback by upvoting and downvoting AI suggestions for continuous learning and iteration loops.